People carrying high levels of visceral fat tend to have protruding abdomens and may be at greater risk for health conditions like heart disease, diabetes and elevated cholesterol levels – not to mention difficulty managing their weight and losing it altogether.
Your genes and age both play an integral part in where your body stores fat. When in a calorie deficit, however, the body typically utilizes visceral fat first as fuel to burn off.
How to Lose Visceral Fat
Visceral fat can be a serious health risk because its deposits release chemicals that disrupt normal body processes and increase your risk for chronic inflammation, diabetes and heart disease. Fat cells produce various molecules; those produced by visceral fat tend to be more toxic. They also constrict blood vessels leading to high blood pressure – all this makes visceral fat harder to manage with diet and regular exercise – although both types can be reduced with regular healthy living practices and exercise regimen. Thankfully both types of fat can be addressed effectively through lifestyle modifications and healthy living practices! Luckily both types can be reduced by adopting healthy eating practices along with regular physical exercise!
Genetics play an essential part in your ability to shed visceral fat, but diet and lifestyle play an equally essential part. An unhealthy diet that includes sugary and fatty foods as well as physical inactivity increases visceral fat storage.
Dietary changes can help you reduce visceral fat by increasing the amount of dietary fibre you ingest. Be sure to eat plenty of whole grains, fruits and vegetables along with lean proteins for best results. Be wary of additional sugars, processed foods as well as trans fats and sodium intake – they all can contribute to visceral fat accumulation in the abdominal region.
Ketogenic diets such as the Atkins Diet can also help you decrease visceral fat. They allow your body to metabolize fat more effectively, leading to greater weight loss than conventional dieting methods.
Moderate intensity aerobic exercises like brisk walking, running, cycling or swimming can help you shed visceral fat more effectively. Try to allocate at least 30 minutes each day for this type of cardio training.
Eating a healthy and well-balanced diet that contains plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables is also one effective way to combat visceral fat accumulation. Tracking food using an app like MyFitnessPal can help identify areas for improvement while another effective approach is increasing consumption of soluble fibre such as found in oatmeal, beans, lentils nuts or sweet potatoes – studies have demonstrated that increasing daily soluble fibre consumption by 10 grams could result in lower visceral fat accumulation rates.

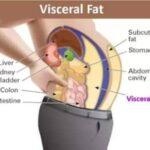
Subcutaneous Fat
Most people’s body fat consists of subcutaneous layers, located directly under their skin. If you pinch your belly, any soft spot is subcutaneous fat; visceral fat, however, resides deep within abdominal walls and covers vital organs such as liver and intestines; this form of visceral fat causes your stomach to protrude and gives it an apple shape; additionally it produces chemicals and hormones which may be detrimental to health.
Your genes dictate how much of this type of fat you begin with and environmental factors determine its development over time, but you can control its accumulation by following a low-calorie diet rich in lean proteins, fruits and vegetables, whole grains and plenty of fibre, along with regular physical activity that elevates your heart rate.
Fatty tissue in your body serves many functions, from helping store energy and keep organs warm to providing lubrication, protection, shock absorption and helping regulate your metabolism by producing enzymes to use carbohydrates, proteins and fats more efficiently.
Adipose tissue serves another important purpose by keeping skin from sagging and providing insulation that regulates body temperature. Lipids produced by subcutaneous fat cells also act as cushions to protect nerves and muscles from damage while transporting nutrients and hormones between muscle layers and skin layers.
Exercise regularly and follow a balanced diet low in processed and saturated fats. Also drinking plenty of water, limiting alcohol consumption, getting adequate restful sleep and adding stress-relief activities into daily life may also help. Sugar — which can be found in many processed food items including fruit juice — contributes to visceral fat storage; one study indicated that daily consumption of more than 20 grams of added sugar increased abdominal obesity risk by 5%.
Diet
At least 90% of your fat is subcutaneous — lying just beneath the skin’s surface — while visceral fat is found deeper within your belly, surrounding organs. While you cannot directly feel or see visceral fat accumulations, doctors can measure abdominal circumference to determine if they have excess visceral fat deposits.
Visceral fat can build up in some people to the point that it increases your risk for cardiovascular disease and other health problems, while blocking blood flow to your brain and leading to inflammation that could be related to Alzheimer’s or mental illnesses such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
To reduce visceral fat, you can employ similar diet and exercise strategies that helped you shed excess pounds in the first place. These strategies include eating a diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, low-fat dairy and fruits and vegetables as well as limiting processed food products like trans fats, refined sugars and sodium. A ketogenic diet may be especially helpful at helping your body burn off visceral fat for fuel; intermittent fasting, getting plenty of restful sleep at night and managing stress may all also contribute significantly.
Visceral fat is one of the first things to go when trying to shed excess pounds, since its resistance to changes in caloric intake is more profound. If you want to lose visceral fat effectively, committing yourself to a long-term diet and exercise plan can be crucial.
Aerobic exercises such as jogging, swimming and biking are highly effective ways to help reduce overall body fat – including visceral fat. By increasing your heart rate and burning more calories with each aerobic session and decreasing calorie consumption, aerobic exercises can help shed visceral fat more efficiently than ever before. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor waistline size and visceral fat percentage is recommended so as to determine whether any lifestyle changes you make are working effectively or need further adjustment.
Exercise
Visceral or subcutaneous fat storage is determined largely by your genetics; diet and exercise also play an integral part. People with “pot bellies,” known as apple shapes, typically store more visceral fat than pear shapes; this deeper form of fat wraps around abdominal organs and produces hormones and chemicals which negatively impact health, increasing risks associated with heart disease, high cholesterol, diabetes and other illnesses.
Visceral fat can be effectively eliminated through exercise and eating healthily. To start off, calculate your daily calorie needs using an online calculator or speaking to a dietitian and consume less than that number in terms of nutrients-rich foods such as lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Exercise may also aid with insulin sensitivity issues and inflammation reduction for positive overall health benefits.
As you lose weight through diet and exercise, your body will naturally prioritize getting rid of visceral fat first – this may delay weight loss as quickly as expected; but keep in mind that your body is still making strides to reduce visceral fat deposits while improving health overall.
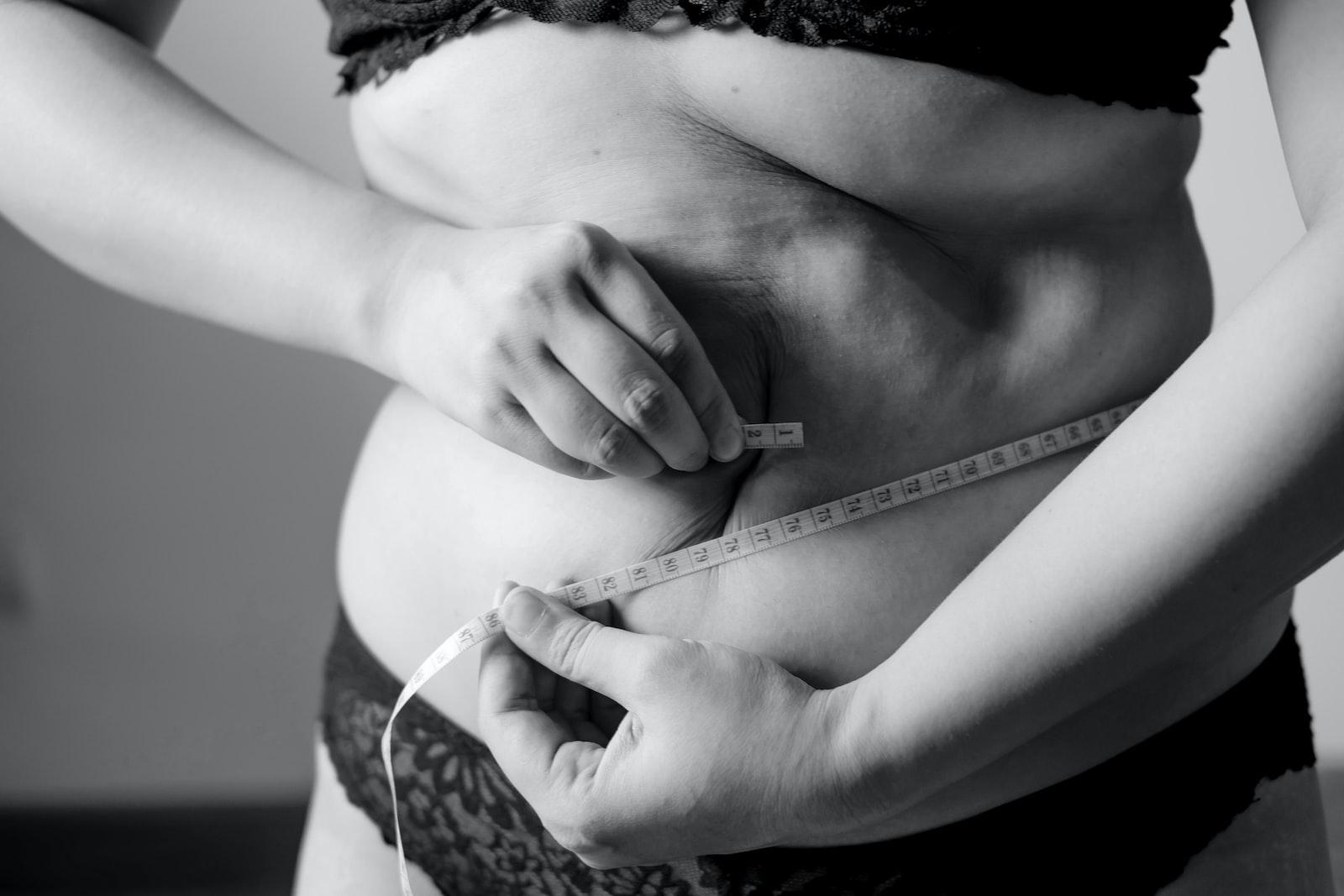
If you’re worried about visceral fat accumulation, one effective way to measure it is with a tape measure wrapped around your waist. Women should make sure to place it no lower than their hip bones or ilium; men should place the tape no higher than the navel. A waist measurement of 40 inches for women and 35 inches for men indicates having high levels of visceral fat which could be contributing to health risks; your physician can conduct more accurate assessments using tests like blood or urine samples while providing advice regarding lifestyle modifications that may help prevent or treat it effectively.