Bananas provide an instantaneous boost of energy that can keep you on track to meet your fitness goals. Packed full of potassium, pectin, fiber and magnesium as well as vitamins C and B6, bananas can provide all-round nourishment.
Foods containing resistant starch have a low glycemic index as their fiber-like effects help lower glycemia levels and promote sleepiness. Furthermore, they’re an excellent source of tryptophan, an amino acid essential for sleep regulation.
1. They are high in potassium
Bananas are packed with potassium, an essential mineral for muscle function and cardiovascular wellbeing. Potassium also acts as an electrolyte to keep us hydrated during strenuous workouts; one banana provides 11% of men’s recommended daily intake while 16% is required of women. Other potassium-rich foods include lima beans and beet greens.
Eating foods rich in potassium and fiber is proven to reduce visceral fat by slowing digestion. This allows you to feel full without overeating or cravings; plus potassium helps regulate blood sugar and reduce inflammation within the body!
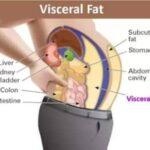
Visceral fat is the type of accumulated body fat stored within and surrounding organs in your abdomen. Compared to subcutaneous fat, which is visible on your skin surface, visceral fat poses greater health risks; eating healthily and engaging in regular physical activity can help combat visceral fat and help you burn it and lose weight more efficiently.
Belly fat can result from multiple causes, such as poor nutrition and lifestyle choices as well as genetics or age. To get rid of belly fat effectively, it’s crucial to limit processed food consumption while increasing fruits and vegetable consumption while getting plenty of rest and physical exercise. To do this effectively.
Bananas are not only rich sources of potassium; they’re also an excellent source of soluble fiber – which helps combat visceral fat by suppressing appetite and keeping gut bacteria happy and healthy. A medium-sized banana provides 3 grams of soluble fiber – that’s 10% of your recommended daily amount! Other dietary sources of soluble fiber include flaxseeds, chia seeds, beans & legumes as well as whole grains.
Bananas are an excellent source of vitamin B6, an essential nutrient for cell metabolism. Furthermore, bananas also provide vitamin C, dietary fibre and manganese; and are low in sodium with no cholesterol or fat content making them the perfect snack to have handy when feeling peckish! You can enjoy eating bananas by themselves or add them into smoothies with other fruit and vegetables for an energy boost!
2. They are high in fiber
Bananas contain high amounts of fiber, an essential nutrient for digestive health. Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance that slows down digestion and lowers blood sugar spikes; while insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool for easier passage through bowels. Furthermore, bananas also contain prebiotics – carbs which don’t get digested but serve as food for the beneficial bacteria living in your colon – which help to support gut microbiomes while possibly decreasing obesity risk.
Bananas rank low on the glycemic load scale, with most varieties falling around 11. This makes them an excellent food option to help promote weight loss by filling you up without adding unnecessary calories and helping increase satiety thanks to fiber in their composition.
Consideration should be given when purchasing bananas: greener varieties contain higher levels of resistant starch, an indigestible carb that acts like dietary fiber to aid with constipation. As soon as they ripen, the resistant starch breaks down and changes into other carbohydrates.
One fascinating study revealed that giving constipated mice resistant starch from bananas helped speed up their stool movements. Researchers suspect this may be because resistant starch helped create an optimal environment for gut bacteria within their bodies.
One medium banana provides more than the recommended daily fiber intake for women and men combined. Plus, bananas contain potassium – another essential nutrient in fighting visceral fat.
Visceral fat, or belly fat, is often difficult to shed. Its origins may lie anywhere between lack of exercise, an unhealthy diet, genetics and genetic predisposition – however bananas can help prevent visceral fat from accumulating by providing energy between meals as an energy boost snack.
3. They are low in calories
Some foods can contribute to abdominal weight gain if consumed excessively; these include those high in calories and sugar content. But bananas are low in both; when consumed in moderation, they won’t contribute to stomach fat accumulation or weight gain.
Glycemic index values vary with portion sizes; small bananas fall at 11 while larger ones can go closer to 20 on this index. Green bananas can still be an effective weight-loss food due to their resistant starch content which prevents carbohydrates from being absorbed in your digestive tract and instead encourages your body to use fat stores as energy sources.
Bananas are low in calorie, rich in potassium and multivitamin content and an ideal way to satisfy sweet tooth while feeling satisfied for longer. You can add them into a smoothie along with other fruits like berries, ginger or chia seeds for additional benefits.
People often believe bananas to be bad for them, however this is simply untrue. A banana contains essential vitamins and nutrients essential to maintaining a healthy diet including potassium and fiber. Furthermore, bananas provide vitamin C which may help regulate your blood pressure; however it’s best not to consume more than 3-4 bananas daily for maximum benefit.
Visceral fat, commonly found deep within the belly, can pose serious health risks. There are various methods available for getting rid of belly fat – exercise and dieting being two effective solutions; in particular limiting processed food consumption through eating more vegetables and whole grains along with lean proteins. You could also increase soluble fiber intake – something found in fruits, vegetables, legumes and flaxseeds!
4. They are low in fat
Bananas are low in fat, and when consumed in moderation do not contribute to weight gain. However, other factors could still play a part in weight gain including lack of exercise, unhealthy eating habits and genetics. Still, bananas make for a nutritious and delicious addition to any healthy diet plan!
Banans contain many carbohydrates, with most coming in the form of fiber. This means they do not raise blood sugar levels as quickly as other forms of carbs do, plus their combination with protein helps the body feel full and satisfied.
Bananas rank lower on the Glycemic Index than most fruits and vegetables, though still higher than white rice (and lower than oatmeal). This may be due to their starches not breaking down so quickly and therefore being less likely to cause spikes in blood glucose levels.
Bananas have an exceptional low glycemic index (GI) value and also possess a moderate glycemic load (GL). A medium-sized banana has a GI value of 12, which falls on the low side for most foods; however, note that banana GI values depend upon portion size – smaller bananas typically fall towards the lower end of this scale with a GI score closer to 11.
Green bananas contain high concentrations of resistant starch, which acts like dietary fiber in the digestive tract and is key in helping reduce bloating and belly fat while aiding weight loss. They also contain ample potassium and vitamin C.
As bananas ripen, their flavor sweetens and their resistant starch content decreases, so eating green bananas or adding them to smoothies or shakes to reap their prebiotic benefits will promote a healthy gut and immune system, improve digestion and decrease blood pressure – ultimately helping prevent chronic health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes and stroke.