If you are trying to reduce your body fat and you’re wondering if it’s easier to lose visceral fat than other types of body fat, then you’ve come to the right place. Visceral fat is a type of fat that lies deep inside the abdominal region and is often harder to remove than the subcutaneous or skin fat. It is also linked to serious health problems such as cancer and heart disease.
Trans fats increase storage of visceral fat
Trans fats are a type of fatty acid that is found in many foods. These fats are added to liquid oils in an industrial process and are considered to be less healthy than other forms of fat. They are commonly found in snacks, crackers, baked goods, and even vegetable shortenings.
When we consume trans fats in the diet, they are incorporated into phospholipids and cholesteryl esters. In contrast, saturated fatty acids are preferentially incorporated into position 1 of phosphoacylglycerols. This results in an uneven distribution of trans fatty acids in the body. It is therefore important to limit the amount of trans fats in our diet.
The concentration of trans fatty acids in tissues is lower than in the diet. For example, the average person’s trans fatty acid intake is only approximately 8 percent of the calories they eat. But when this amount is stored in the abdominal cavity, it can lead to health problems. Because of its location near the portal vein, visceral fat can increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Trans fats are also associated with increased levels of total cholesterol. However, they are not a primary cause of coronary heart disease. Research has shown that reducing the amount of trans fatty acids in your diet can reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease, as well.

Although trans fats are an issue, they are not the only cause of belly fat. Other factors that contribute to belly fat include an unhealthy lifestyle, a genetic predisposition, and environmental conditions. If you think that you might have excess abdominal fat, you should see a doctor and get a check-up. Your healthcare provider can also help you create a plan for reducing the amount of visceral fat you have.
If you do decide to start a workout program, you can trim your waistline by performing high-intensity interval training. This form of exercise will burn fat faster, and you can use resistance or aerobic exercises to do this. A popular workout is the HIIT cycle. You will alternate between a quick burst of intensity and then a slow pause.
To avoid accumulating excess body fat, you should keep your weight in a healthy range. You should also maintain a balanced diet. Ideally, you should be consuming about 20% to 35% of your daily calories from fat. Soybeans, nuts, and avocados are all great sources of unsaturated fatty acids.
Another way to avoid belly fat is to pay attention to your sleep. Studies have shown that those who sleep fewer hours at night accumulate more visceral fat than those who sleep a minimum of seven hours. Sleep also affects the way you metabolize food.
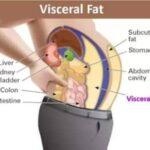
Visceral fat is located deep within your abdomen and around your organs. It is not visible to the naked eye, but it is important for your health. Visceral fat is responsible for promoting inflammation, which can increase the risk of several chronic diseases.
It increases the risk of heart disease and cancer
Visceral fat, or abdominal adipose tissue, is an important risk factor for heart disease and cancer. These adipose tissues produce different hormones and chemicals, and are close to vital organs. It is a good idea to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly to keep this organ at a manageable level. A doctor can help to measure the size and quantity of your visceral adipose tissue and make recommendations for lifestyle changes that may decrease the amount.
Excess body fat is a major risk factor for many diseases, including cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cancer. Some studies have even shown that overweight people are at higher risk for certain types of cancer. However, the link between obesity and cancer is still a subject of debate. Research is being conducted to identify the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying this association.
Several studies have demonstrated the existence of an increased risk of cancer for overweight or obese individuals, but the exact mechanisms remain unknown. One study found that women who were not obese were just as likely to die from cancer as women who were overweight. In contrast, obese men were more likely to develop prostate and colon cancers.
There is no doubt that obese people are at a greater risk for diabetes, heart attacks, and osteoarthritis. In fact, the American Heart Association reports that each 4.3-point increase in body mass index is associated with a 13 percent higher risk of cardiovascular events. Overweight women who gained at least 20 kilograms in five years had a graded increase in their risk of heart disease compared to thinner women.
Several animal studies have reported that the presence of visceral adipose tissues is associated with various metabolic processes and alterations in immune responses. For example, adipose tissue releases several adipocytokines, which are proteins that affect the rate of metabolism and the amount of fat that can be stored. They can also change the way that cholesterol is produced. As well, chemicals released by adipose tissue may play a role in a variety of other maladies, including blood clotting.
A recent study suggested that visceral adipose cells may contribute to an increased occurrence of cancer. Specifically, an inflammatory process of the adipose tissue has been identified, in which classically activated M1 macrophages produce pro-inflammatory cytokines. Other substances that may be released by adipose tissues include reactive oxygen species and interleukin 6 (IL-6). The presence of these and other cytokines may explain why obese people are at a higher risk for a number of conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Although the connection between obesity and a number of cancers remains unclear, there are some promising developments in the field. For instance, there are shared pharmacological treatments that might lower the risk of both diseases. But it will take more research to uncover the exact mechanisms linking the two, and public health policymakers need to do more to educate the general public on this topic.
It’s easier to lose than subcutaneous fat
Visceral fat and subcutaneous fat are two kinds of fat that are deposited in the body. Visceral fat is located deep within the abdominal cavity, and it surrounds the internal organs. Subcutaneous fat is found just beneath the skin, and it’s easy to pinch and feel. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease is increased by excessive amounts of visceral fat. Despite the dangers, it is still possible to lose weight by shedding it. In fact, visceral fat is more difficult to lose than subcutaneous fat.
If you’re trying to reduce your weight, you probably know that you should exercise. But it’s important to understand that you should also watch your diet. This is because the right kind of food can help you lose subcutaneous belly fat.
You should try to consume as much lean protein as possible. Try to limit your consumption of added sugars. Also, keep your alcohol intake low. Avoid processed foods that contain trans fats. Moreover, eat more whole grains. Eating a healthy diet will help you get rid of fat from other parts of your body.
Visceral fat and subcutaneous fat are similar in that they both produce more cytokines, a substance that causes inflammation in your body. However, subcutaneous fat can be beneficial to you, as it provides a protective layer for the deeper structures of your body. It can also increase the production of helpful molecules, like hormones.
Both types of fat can be detrimental to your health, though. When you have excess subcutaneous fat, it is more likely to increase your risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, and liver disease. On the other hand, visceral fat is associated with higher rates of type 2 diabetes, stroke, heart attack, and gallbladder surgery. While it’s a good idea to lose a few pounds, it’s more important to avoid gaining back any of the weight you lose.
Diet and exercise can make a big difference in the size of your body. However, it’s a good idea to speak to your doctor to determine if you’re at a high risk for developing certain health problems. A doctor can tell you if you’re at risk for conditions that could affect your health, and he can also check your vital signs.
It’s best to lose your fat in a gradual way. For example, you should start by reducing your calorie intake by 500 to 1,000 calories a day. By doing this, you should be able to lose about one to two pounds a week. Having a balanced diet with healthy portions of fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains will help you achieve this goal.
Exercise helps you to burn off subcutaneous belly fat. Especially, it’s a good idea to do strength training. Moreover, aerobic activities like biking or walking are also recommended. Your body will start to use its fat reserves to provide energy to your muscles.