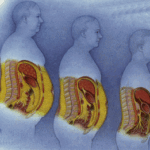
Lower belly fat can make it more challenging to fit into your favorite jeans and carries health risks that could eventually lead to disease.
People develop belly fat for various reasons, but improving your diet and exercise habits may help. One easy step you can take to combat it is swapping out sugary drinks for fruit juices as part of a healthier alternative beverage plan.
Subcutaneous fat
Subcutaneous fat, also known as subcutaneous adipose tissue, lies just beneath the skin’s surface and when present can lead to love handles or an expanded waistline.
It is an integral component of our bodies because it stores energy and maintains muscle and blood vessel health, producing hormones and maintaining internal body temperature regulation.
Subcutaneous fat can be easily reduced with a diet low in calories and consistent exercise such as running, cycling, swimming and brisk walking – these exercises will help your heart rate to elevate and will assist with burning off subcutaneous fat faster.
However, changing your eating habits and increasing physical activity aren’t enough. Stress management and taking measures that minimize other causes for abdominal fat may also help.
Belly fat has been linked with increased risks for diabetes and heart disease, as well as leading to higher levels of inflammation – increasing your chances of becoming sick more easily.
According to the Mayo Clinic, losing visceral and subcutaneous fat can help protect you against health risks while improving overall wellness. Your genetic makeup as well as lifestyle factors like diet and physical activity will have an effect on how much body fat there is in your system.
To reduce belly fat, start by swapping carbohydrates for protein and engaging in aerobic exercises that reduce appetite while encouraging you to consume healthier food options.
First, understand why you overeat or crave unhealthy snacks when stressed. Your brain might be trying to calm you down or give a mental pick-me-up; whatever it is, overeating may not be helpful in either instance.
Understanding what triggers overeating will make breaking the cycle and losing belly fat much simpler. Consult a dietician or doctor for additional support if needed.
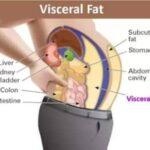
Visceral fat
Visceral fat is a type of abdominal fat stored around organs such as the pancreas and duodenum. It becomes an issue in people who are overweight or obese, increasing their risk for various health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Visceral fat can contain hormones that have an adverse effect on health, so it’s crucial that it’s managed well. Hormones produced by this form of fat may increase your risk for asthma, heart disease and certain cancers.
One way to shed visceral fat is to increase insulin sensitivity and lower inflammation. This will enable your body to use fat as fuel instead of carbs for energy, helping it reach weight loss more quickly.
Exercise regularly as another way of reducing visceral fat. Studies have demonstrated that increasing physical activity can significantly decrease visceral fat even without weight loss.
Regular exercise can also benefit your health in other ways. For example, exercising can lower your risk of heart disease and diabetes while strengthening your immune system and decreasing cholesterol in your bloodstream.
Reduce visceral fat by eating a diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains and fruits and vegetables. Also try limiting your consumption of trans fats, refined sugars and sodium.
If you are concerned about how much body fat you have, visit your physician for a check-up. They can perform a full body fat analysis and tailor an effective program specifically for you, including how to exercise effectively so as to lose abdominal fat. They may even provide training on proper abdominal training techniques to speed the process along.
Fiber
Fiber is one of the most undervalued nutrients you can add to your diet, helping keep you feeling satiated while controlling weight and even managing diabetes.
Problematic is that most of us do not consume enough fiber to reap its many advantages. Luckily, there are plenty of food items with fiber that you can enjoy!
Included among them are whole grains, fruits, vegetables and legumes – but it is crucial that you understand how much fiber you should be getting daily.
Most healthy individuals need at least 25 grams of fiber daily in order to remain in good health and maintain a stable weight. While many individuals fail to meet this recommendation, it is still possible to increase intake without experiencing adverse side effects like gas, bloating and diarrhea.
Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, which aids digestion by slowing it down, as well as helping lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels, reduce bloating, and aid constipation.
If you’re trying to drop belly fat, soluble fiber may be your ally. It can be found in many fruits, vegetables, grains and seeds such as flaxseeds, beans and oats.
While whole, unprocessed foods provide optimal sources of fiber, there are supplements you can take to increase your daily consumption. Some contain psyllium husk which has been proven to decrease belly fat while increasing insulin sensitivity.
Soluble fiber helps promote a healthy gut bacteria balance. According to research, having more varieties of helpful bacteria may reduce your risk of belly fat due to prebiotic effects from soluble fiber acting as food for these microbes that then produces short-chain fatty acids resulting in decreased body fat.
Sugar
Sugar is a carbohydrate, meaning that it provides energy to the body in the form of glucose. This glucose travels through blood and directly into every cell throughout your body for quick access.
Food carbohydrates are broken down into glucose and fructose – essential sugars for maintaining our bodies and their proper functioning.
But not all sugars are the same: Some forms of it naturally occur in food while others can be added during processing and preparation.
Gluccose is the predominant form of sugar found in human diet, however other types of sweeteners, including fructose (fruit sugar), lactose and maltose are consumed regularly as well.
Disaccharides can also be found in our diets. These consist of two monosaccharides that combine to create disaccharides containing equal portions of each monosaccharide.
Disaccharides can be found naturally in all green plants and milk, but can also be created using various ingredients as starting points, including molasses.
People often assume all sugars are bad for us; however, different varieties have differing effects on the body.
One of the main issues is how high blood sugar levels cause our bodies to store fat due to how sugar affects our brains.
Sugars can exacerbate cravings and hunger, making weight loss more challenging. This is due to sugar’s effect on insulin levels in your blood, leading to less leptin being released as the “I’m full” signal isn’t activated as efficiently and thus more food being eaten to compensate.
Trans fats
Trans fats are detrimental to health as they increase levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol in your blood, increasing your risk for heart disease and diabetes.
For optimal heart health, the American Heart Association advises limiting trans fat consumption to no more than 1 percent of your total calories (which amounts to roughly two or 2.5 grams daily). You can find out exactly how much trans fat there is in different food items by checking their Nutrition Facts label or ingredients list.
Although certain foods, like butter or margarine, contain trace amounts of trans fats, the majority of our consumption can be found in processed food such as vegetable shortenings, some margarines, cookies, crackers, fried foods (such as doughnuts and French fries) as well as certain packaged snacks.
Dieting to reduce trans fats requires eating fewer processed foods. Choose those made with natural, healthful oils like olive or canola oil and reduce fat usage at home while eating more fresh produce and fruits and vegetables.
Trans fats can have serious health implications; not only are they detrimental, they increase your risk of obesity and insulin resistance – potentially leading to type 2 diabetes.
Trans fats come in various forms, but the most prevalent ones are hydrogenated oils and partially hydrogenated vegetable oils used in frying and baking for making baked goods like doughnuts and French fries greasy.
In 2006, New York City prohibited artificial trans fats and mandated that food service establishments phase them out by 2008. This regulation is an effective way to limit your exposure to these unhealthy fats.