Introduction to Visceral Fat
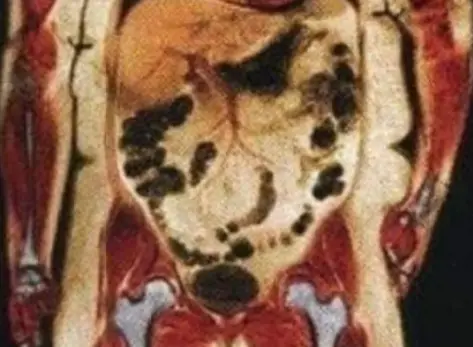
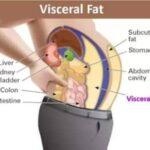
Visceral fat, also known as belly fat, is the fat stored within the abdominal cavity. It surrounds vital organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. While some amount of fat is essential for the body to function properly, an excess of visceral fat can be harmful to your health.
What is Visceral Fat and why is it harmful?
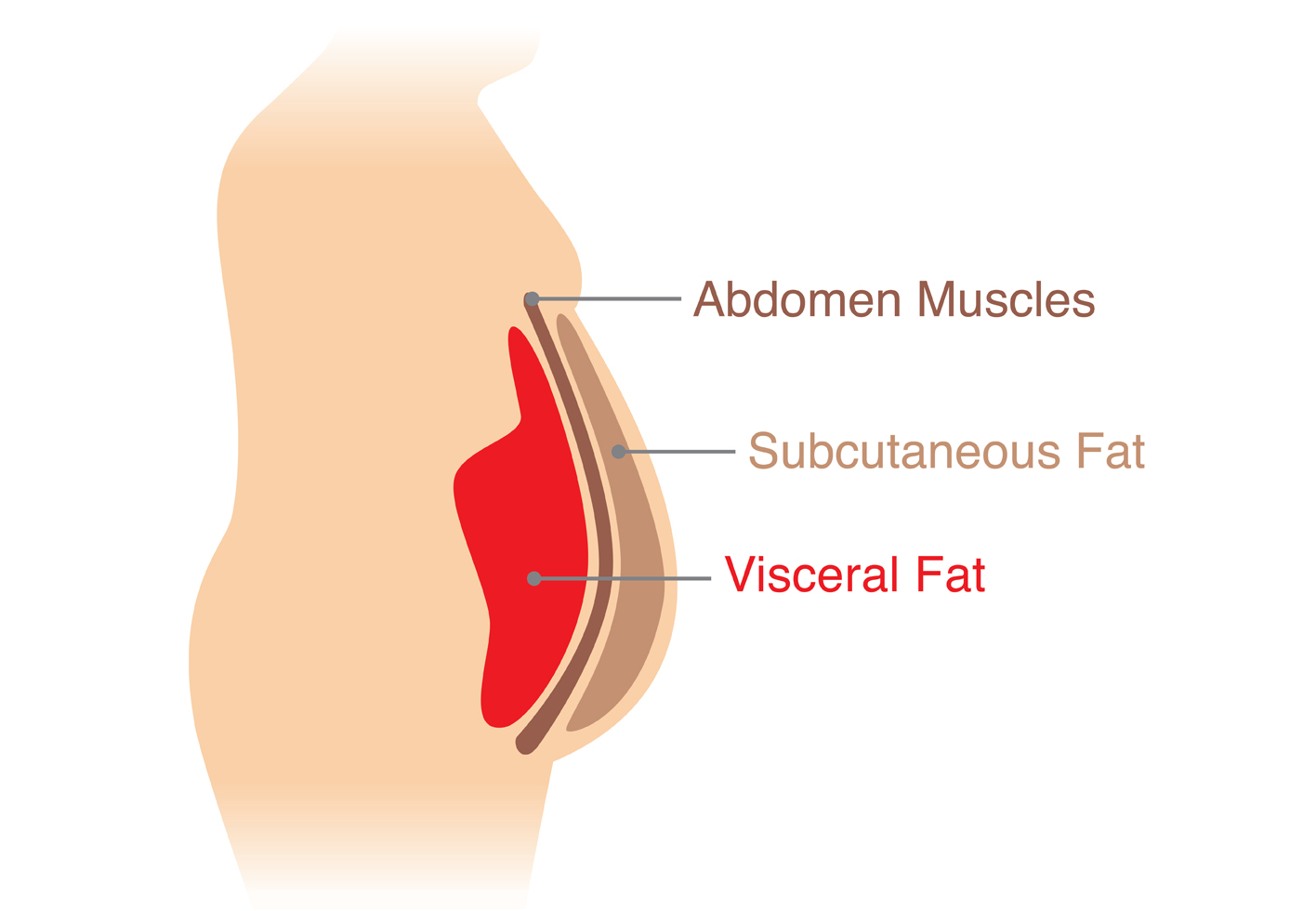
Unlike subcutaneous fat, which is found just beneath the skin, visceral fat is deeper and more dangerous. It releases hormones and inflammatory substances that can increase the risk of serious health conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. It can also impair the body’s ability to regulate insulin, leading to insulin resistance.
Understanding the health risks associated with Visceral Fat
Excess visceral fat has been linked to several health problems, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and an increased risk of stroke. It can also contribute to metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that raise the risk of cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, studies have shown that visceral fat is more strongly associated with insulin resistance and inflammation than subcutaneous fat.
Taking steps to reduce visceral fat, such as engaging in regular exercise and adopting a healthy diet, can help lower your risk of these health issues. It’s important to remember that even if you have a normal weight, you may still have excess visceral fat. Therefore, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced lifestyle and prioritize your overall health and well-being.

Causes and Factors
Factors contributing to the accumulation of Visceral Fat
Visceral fat, commonly referred to as belly fat, is the deep fat that wraps around the internal organs in the abdominal cavity. Several factors contribute to the accumulation of visceral fat in the body, including genetics, age, gender, and hormonal changes. Research has shown that individuals with a family history of obesity are more prone to storing excess fat in the abdomen.
Impacts of lifestyle choices on Visceral Fat levels
Apart from genetic factors, lifestyle choices play a significant role in the accumulation of visceral fat. A sedentary lifestyle, lack of exercise, unhealthy eating habits, excessive alcohol consumption, and high stress levels can contribute to the build-up of visceral fat. Additionally, studies have evidenced that poor sleep patterns and inadequate rest can also impact visceral fat levels.
To reduce visceral fat, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet with portion control, stress management techniques, and good quality sleep is recommended. By making these positive changes, individuals can significantly decrease their visceral fat levels and improve their overall health.
Health Effects
How Visceral Fat affects overall health
Visceral fat, also known as belly fat, is not just a matter of appearance. It has significant effects on a person’s overall health. Unlike subcutaneous fat that sits just beneath the skin, visceral fat is located deeper, surrounding vital organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines.
When there is an excess of visceral fat, it can lead to a number of health problems. The fat cells release inflammatory substances that can increase the risk of developing chronic diseases such as:
Understanding the link between Visceral Fat and chronic diseases
- Cardiovascular disease: Excessive visceral fat increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
- Type 2 diabetes: Visceral fat releases hormones that can interfere with insulin function, leading to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic syndrome: Visceral fat is associated with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high cholesterol, and excess abdominal fat.
- Certain cancers: Studies have shown a link between visceral fat and an increased risk of cancers, including breast, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer.
- Other health issues: Excess visceral fat has also been linked to fatty liver disease, sleep apnea, and problems with fertility and hormonal balance.
It is important to note that even individuals with a healthy body weight can have high levels of visceral fat. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, is key in reducing visceral fat and improving overall health.
Measurement and Assessment
Methods to measure and assess Visceral Fat levels
Visceral fat refers to the fat that accumulates around the organs, such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. To establish the amount of visceral fat in your body, there are several methods that can be employed:
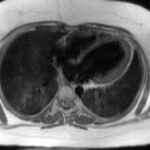
- CT Scan: This medical imaging technique provides a detailed view of the organs and allows for accurate measurement of the amount of visceral fat present.
- Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA): Originally used to measure bone density, DXA scans can also provide an estimate of visceral fat by analyzing the body’s composition.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Similar to a CT scan, an MRI can provide detailed images of the internal organs and measure visceral fat.
Understanding the importance of Visceral Fat tests
It is essential to assess and monitor visceral fat levels because high amounts of this fat have been linked to various health problems, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By regularly measuring and assessing visceral fat, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing their risk of these diseases.
Visceral fat tests also offer insights into the effectiveness of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and can help individuals track their progress towards a healthier body composition. These tests provide valuable information that empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and take the necessary actions to reduce their visceral fat levels.

Strategies for Visceral Fat Reduction
Dietary approaches to reduce Visceral Fat
Visceral fat, also known as belly fat, is not only unsightly but also poses significant health risks. Fortunately, there are dietary approaches that can help you reduce this dangerous fat.
- Choose a balanced diet: Incorporate nourishing foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Reduce calorie intake: Consuming fewer calories than your body needs can lead to both overall weight loss and the reduction of visceral fat.
- Focus on healthy fats: Include foods rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, like avocados, fatty fish, and nuts, which have been associated with a decrease in visceral fat.
Exercise and physical activity for Visceral Fat reduction
Regular exercise and physical activity play a crucial role in reducing visceral fat. Here are some effective strategies:
- Aerobic exercise: Engage in activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming to burn calories and promote overall fat loss, including visceral fat.
- Strength training: Incorporate resistance exercises like weightlifting to build muscle mass. Increased muscle strength can help boost metabolism and reduce visceral fat.
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): Alternating between short bursts of intense exercise and recovery periods has been shown to effectively reduce visceral fat.
Remember, reducing visceral fat requires a comprehensive approach involving both dietary changes and regular exercise. Consistency and discipline are key to achieving long-lasting results.

Lifestyle Changes
Effective lifestyle changes to combat Visceral Fat
Visceral fat, also known as belly fat, is the fat that accumulates around internal organs in the abdominal cavity. It is linked to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. If you are looking to reduce visceral fat, here are some effective lifestyle changes you can make:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet that includes lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary foods, processed snacks, and alcohol.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in aerobic activities such as jogging, swimming, or cycling to burn calories and reduce overall body fat. Incorporate strength training exercises to build lean muscle mass.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to the accumulation of visceral fat. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga.
- Get Enough Sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, leading to weight gain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and help with digestion and metabolism.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can reduce visceral fat and improve your overall health. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
Conclusion
Visceral fat is a dangerous type of fat that is stored deep within the abdominal cavity and surrounds vital organs. It poses a significant risk to health, increasing the chances of developing serious medical conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
Steps to effectively manage and reduce Visceral Fat levels
- Follow a healthy diet: Focus on consuming whole foods, reduce refined sugars and carbs, and increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Incorporate both cardiovascular exercises and strength training into your fitness routine to help burn calories, build muscle, and reduce visceral fat.
- Manage stress levels: Chronic stress can contribute to the accumulation of visceral fat. Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night as insufficient sleep can disrupt hunger hormones and lead to weight gain, including visceral fat.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption: Alcohol can contribute to weight gain and the accumulation of visceral fat. Limit your intake to moderate levels or avoid it altogether.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage and reduce visceral fat levels, improving your overall health and reducing the risk of related diseases. Remember, consistency and patience are key when it comes to achieving long-term results.